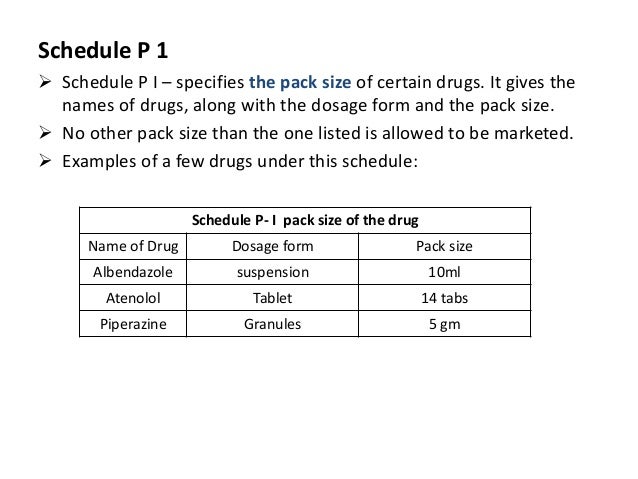
What Is A Schedule 1 Drug
This is the list of Schedule I drugs as defined by the United StatesControlled Substances Act.[1] The following findings are required for drugs to be placed in this schedule:[2]
- The drug or other substance has a high potential for abuse.
- The drug or other substance has no currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States.
- There is a lack of accepted safety for use of the drug or other substance under medical supervision.
Schedule I (or Schedule 1) substances possess no known medicinal benefits, and have a very high potential for addiction. Commonly known as “street drugs,”. This is the list of Schedule I drugs as defined by the United States Controlled Substances Act. The following findings are required for drugs to be placed in this schedule: [2] The drug or other substance has a high potential for abuse. Jan 23, 2015 - Schedule 1 (I) drugs, substances, or chemicals are defined by the federal government as drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse. Schedule 1 (I) drugs are the most dangerous drugs of all the drug schedules with potentially severe psychological or physical dependence.
Except as specifically authorized, it is illegal for any person:
- to manufacture, distribute, or dispense, or possess with intent to manufacture, distribute, or dispense, a controlled substance; or
- to create, distribute, or dispense, or possess with intent to distribute or dispense, a counterfeit substance.[3]
What Is A Schedule 1 Drug Australia
The complete list of Schedule I drugs follows.[1] The Administrative Controlled Substances Code Number for each drug is included.
Opioids[edit]
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 9815 | Acetyl-alpha-methylfentanyl (N-[1-(1-methyl-2-phenethyl)-4-piperidinyl]-N-phenylacetamide) |
| 9601 | Acetylmethadol |
| 9602 | Allylprodine |
| 9603 | Alphacetylmethadol (except levo-alphacetylmethadol also known as levo-alpha-acetylmethadol, levomethadyl acetate, or LAAM) |
| 9604 | Alphameprodine |
| 9605 | Alphamethadol |
| 9814 | Alpha-methylfentanyl (N-[1-(alpha-methyl-beta-phenyl)ethyl-4-piperidyl] propionanilide; 1-(1-methyl-2-phenylethyl)-4-(N-propanilido) piperidine) |
| 9832 | Alpha-methylthiofentanyl (N-[1-methyl-2-(2-thienyl)ethyl-4- piperidinyl]-N-phenylpropanamide) |
| 9606 | Benzethidine |
| 9607 | Betacetylmethadol |
| 9830 | Beta-hydroxyfentanyl (N-[1-(2-hydroxy-2-phenethyl)-4- piperidinyl]-N-phenylpropanamide) |
| 9831 | Beta-hydroxy-3-methylfentanyl (other name: N-[1-(2-hydroxy-2- phenethyl)-3-methyl-4-piperidinyl]-N-phenylpropanamide |
| 9608 | Betameprodine |
| 9609 | Betamethadol |
| 9611 | Betaprodine |
| 9612 | Clonitazene |
| 9613 | Dextromoramide |
| 9615 | Diampromide |
| 9616 | Diethylthiambutene |
| 9168 | Difenoxin |
| 9617 | Dimenoxadol |
| 9618 | Dimepheptanol |
| 9619 | Dimethylthiambutene |
| 9621 | Dioxaphetyl butyrate |
| 9622 | Dipipanone |
| 9623 | Ethylmethylthiambutene |
| 9624 | Etonitazene |
| 9625 | Etoxeridine |
| 9626 | Furethidine |
| 9627 | Hydroxypethidine |
| 9628 | Ketobemidone |
| 9629 | Levomoramide |
| 9631 | Levophenacylmorphan |
| 9813 | 3-Methylfentanyl (N-[3-methyl-1-(2-phenylethyl)-4-piperidyl]-N-phenylpropanamide) |
| 9833 | 3-methylthiofentanyl (N-[(3-methyl-1-(2-thienyl)ethyl-4-piperidinyl]-N-phenylpropanamide) |
| 9632 | Morpheridine |
| 9661 | MPPP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-4-propionoxypiperidine) |
| 9633 | Noracymethadol |
| 9634 | Norlevorphanol |
| 9635 | Normethadone |
| 9636 | Norpipanone |
| 9812 | Para-fluorofentanyl (N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-[1-(2-phenethyl)-4-piperidinyl] propanamide |
| 9663 | PEPAP (1-(-2-phenethyl)-4-phenyl-4-acetoxypiperidine |
| 9637 | Phenadoxone |
| 9638 | Phenampromide |
| 9647 | Phenomorphan |
| 9641 | Phenoperidine |
| 9642 | Piritramide |
| 9643 | Proheptazine |
| 9644 | Properidine |
| 9649 | Propiram |
| 9645 | Racemoramide |
| 9835 | Thiofentanyl (N-phenyl-N-[1-(2-thienyl)ethyl-4-piperidinyl]-propanamide |
| 9750 | Tilidine |
| 9646 | Trimeperidine |
| 9821 | Acetyl Fentanyl (N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylacetamide)[4] |
Opium derivatives[edit]
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 9319 | Acetorphine |
| 9051 | Acetyldihydrocodeine |
| 9052 | Benzylmorphine |
| 9070 | Codeine methylbromide |
| 9053 | Codeine-N-Oxide |
| 9054 | Cyprenorphine |
| 9055 | Desomorphine |
| 9145 | Dihydromorphine |
| 9335 | Drotebanol |
| 9056 | Etorphine (except hydrochloride salt) |
| 9200 | Heroin (diacetylmorphine) |
| 9301 | Hydromorphinol |
| 9302 | Methyldesorphine |
| 9304 | Methyldihydromorphine |
| 9305 | Morphine methylbromide |
| 9306 | Morphine methylsulfonate |
| 9307 | Morphine-N-Oxide |
| 9308 | Myrophine |
| 9309 | Nicocodeine |
| 9312 | Nicomorphine |
| 9313 | Normorphine |
| 9314 | Pholcodine |
| 9315 | Thebacon |
Hallucinogenic or psychedelic substances[edit]
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 7249 | Alpha-Ethyltryptamine (αET) |
| 7391 | 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-amphetamine (DOB) |
| 7392 | 4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B) |
| 7396 | 2,5-dimethoxyamphetamine (DOA) |
| 7399 | 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylamphetamine (DOE) |
| 7348 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(n)-propylthiophenethylamine (2C-T-7), its optical isomers, salts and salts of isomers |
| 7411 | 4-methoxyamphetamine (PMA) |
| 7401 | 5-methoxy-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MMDA) |
| 7395 | 4-methyl-2,5-dimethoxyamphetamine (DOM; STP) |
| 7400 | 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA, Sassafrass) |
| 7405 | 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, Ecstasy, Molly) |
| 7404 | 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-ethylamphetamine (MDEA; MDE) |
| 7402 | N-hydroxy-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (N-hydroxy MDA) |
| 7390 | 3,4,5-trimethoxyamphetamine (TMA) |
| 7431 | 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-methoxy-3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]indole; 5-MeO-DMT) |
| 7432 | Alpha-methyltryptamine (αMT) |
| 7433 | Bufotenine |
| 7434 | Diethyltryptamine (DET) |
| 7435 | Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) |
| 7439 | 5-methoxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamine (5-MeO-DIPT), its isomers, salts and salts of isomers |
| 7260 | Ibogaine |
| 7315 | Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) |
| 7360 | Marijuana or hemp, including cannabis resin |
| 7350 | Marijuana extracts; hemp extracts; cannabinoids[5] |
| 7381 | Mescaline |
| 7374 | Parahexyl |
| 7415 | Peyote |
| 7482 | N-ethyl-3-piperidyl benzilate |
| 7484 | N-methyl-3-piperidyl benzilate |
| 7437 | Psilocybin |
| 7438 | Psilocin |
| 7370 | Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) |
| 7455 | Ethylamine analog of phencyclidine (Eticyclidine; PCE) |
| 7458 | Pyrrolidine analog of phencyclidine (PCPy) |
| 7470 | Thiophene analog of phencyclidine (TCP) |
| 7473 | 1-[1-(2-thienyl)cyclohexyl]pyrrolidine (TCPy) |
| 1248 | 4-methylmethcathinone (Mephedrone) |
| 7535 | 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) |
| 7509 | 2-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylphenyl)ethanamine (2C-E) |
| 7508 | 2-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)ethanamine (2C-D) |
| 7519 | 2-(4-Chloro-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethanamine (2C-C) |
| 7518 | 2-(4-Iodo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethanamine (2C-I) |
| 7385 | 2-[4-(Ethylthio)-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl]ethanamine (2C-T-2) |
| 7532 | 2-[4-(Isopropylthio)-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl]ethanamine (2C-T-4) |
| 7517 | 2-(2,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)ethanamine (2C-H) |
| 7521 | 2-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-nitro-phenyl)ethanamine (2C-N) |
| 7524 | 2-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(n)-propylphenyl)ethanamine (2C-P) |
| 7540 | 3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-methylcathinone (Methylone) |
Depressants[edit]
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 2010 | gamma-Hydroxybutyric acid (GHB; sodium oxybate; sodium oxybutyrate) except formulations in an FDA-approved drug product are Schedule III |
| 2572 | Mecloqualone |
| 2565 | Methaqualone |
What Makes A Schedule 1 Drug
Stimulants[edit]
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 1585 | Aminorex (aminoxaphen; 2-amino-5-phenyl-2- oxazoline; or 4,5-dihydro-5-phenly-2-oxazolamine) |
| 7493 | N-benzylpiperazine (some other names: BZP; 1-benzylpiperazine), its optical isomers, salts and salts of isomers |
| 1235 | Cathinone |
| 1503 | Fenethylline |
| 1237 | Methcathinone (Some other names: 2-(methylamino)-propiophenone; alpha-(methylamino)propiophenone; 2-(methylamino)-1-phenylpropan-1-one; alpha-N-methylaminopropiophenone; monomethylpropion; ephedrone; N-methylcathinone; methylcathinone; AL-464; AL-422; AL-463 and UR1432), its salts, optical isomers and salts of optical isomers |
| 1590 | (+/-)cis-4-methylaminorex |
| 1475 | N-ethylamphetamine |
| 1480 | N,N-dimethylamphetamine (also known as N,N-alpha-trimethyl-benzeneethanamine; N,N-alpha-trimethylphenethylamine) |
Cannabimimetic agents[edit]
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 7297 | 5-(1,1-dimethylheptyl)-2-[(1R,3S)-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]-phenol (CP-47,497) |
| 7298 | 5-(1,1-dimethyloctyl)-2-[(1R,3S)-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]-phenol (cannabicyclohexanol or CP-47,497 C8-homolog) |
| 7118 | 1-pentyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-018 and AM678) |
| 7173 | 1-butyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-073) |
| 7019 | 1-hexyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-019) |
| 7200 | 1-[2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl]-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-200) |
| 6250 | 1-pentyl-3-(2-methoxyphenylacetyl)indole (JWH-250) |
| 7081 | 1-pentyl-3-[1-(4-methoxynaphthoyl)]indole (JWH-081) |
| 7122 | 1-pentyl-3-(4-methyl-1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-122) |
| 7398 | 1-pentyl-3-(4-chloro-1-naphthoyl)indole (JWH-398) |
| 7201 | 1-(5-fluoropentyl)-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole (AM2201) |
| 7694 | 1-(5-fluoropentyl)-3-(2-iodobenzoyl)indole (AM694) |
| 7104 | 1-pentyl-3-[(4-methoxy)-benzoyl]indole (SR-19 and RCS-4) |
| 7008 | 1-cyclohexylethyl-3-(2-methoxyphenylacetyl)indole 7008 (SR-18 and RCS-8) |
| 7203 | 1-pentyl-3-(2-chlorophenylacetyl)indole (JWH-203) |
Temporary/emergency listings[edit]
These items are listed by the Secretary of Health and Human Services pursuant to 21 CFR 1308.49.[6][7]
| ACSCN | Drug |
|---|---|
| 7144 | (1-pentyl-1H-indol-3-yl)(2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropyl)methanone, its optical, positional, and geometric isomers, salts and salts of isomers (UR-144, 1-pentyl-3-(2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropoyl)indole) |
| 7011 | [1-(5-fluoro-pentyl)-1H-indol-3-yl](2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropyl)methanone, its optical, positional, and geometric isomers, salts and salts of isomers (5-fluoro-UR-144, 5-F-UR-144, XLR-11, 1-(5-fluoro-pentyl)-3-(2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropoyl)indole) |
| 7048 | N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide, its optical, positional, and geometric isomers, salts and salts of isomers (APINACA, AKB-48) |
| 7222 | Quinolin-8-yl 1-pentyl-1H-indole-3-carboxylate (QUPIC, PB-22)[8] |
| 7225 | Quinolin-8-yl 1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate (5-fluoro-PB-22; 5F-PB-22)[8] |
| 7012 | N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-FUBINACA)[8] |
| 7035 | N-(1-amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (ADB-PINACA)[8] |
| 7031 | N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-CHMINACA)[9] |
| 7023 | N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-PINACA)[9] |
| 7024 | [1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl](naphthalen-1-yl)methanone (THJ-2201)[9] |
| 7538 | 2-(4-iodo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-(2-methoxybenzyl)ethanamine (25I-NBOMe; 2C-I-NBOMe; 25I; Cimbi-5)[10] |
| 7537 | 2-(4-chloro-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-(2-methoxybenzyl)ethanamine (25C-NBOMe; 2C-C-NBOMe; 25C; Cimbi-82)[10] |
| 7536 | 2-(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-(2-methoxybenzyl)ethanamine (25B-NBOMe; 2C-B-NBOMe; 25B; Cimbi-36)[10] |
| 9547 | 3,4-dichloro-N-[2-(dimethylamino)cyclohexyl]N-methylbenzamide) (U-47700)[11] |
| 9821 | Acetylfentanyl (N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylacetamide)[12] |
| 9834 | N-(1-Phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylfuran-2-carboxamide (furanyl fentanyl)[13] |
| 7034 | 2-(1-(5-Fluoropentyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethylbutanoate (5F-ADB, 5F-MDMB-PINACA)[14] |
| 7033 | Methyl 2-(1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamido)-3-methylbutanoate (5F-AMB)[14] |
| 7049 | N-(Adamantan-1-yl)-1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (5F-APINACA, 5F-AKB48)[14] |
| 7010 | N-(1-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (ADB-FUBINACA)[14] |
| 7042 | Methyl 2-(1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethylbutanoate (MDMB-CHMICA, MMB-CHMINACA)[14] |
| 7020 | Methyl 2-(1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethylbutanoate (MDMB-FUBINACA)[14] |
| 9811 | Acryl fentanyl ((N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylacrylamide); Acryloylfentanyl)[15] |
| 9816 | N-(2-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)propionamide (Ortho-fluorofentanyl or 2-fluorofentanyl)[16] |
| 9822 | Butyryl Fentanyl (N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylbutyramide, N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylbutanamide)[17] |
| 9824 | 4-Fluoroisobutyryl fentanyl ((N-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)isobutyramide) or Para-fluoroisobutyryl fentanyl)[18] |
| 9825 | 2-methoxy-N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylacetamide (Methoxyacetyl fentanyl)[16] |
| 9836 | Beta-hydroxythiofentanyl (N-[1-[2-hydroxy-2-(thiophen-2-yl)ethyl]piperidin-4-yl]-N-phenylpropionamide, N-[1-[2-hydroxy-2-(2-thienyl)ethyl]-4-piperidinyl]-N-phenylpropanamide)[17] |
| 9843 | N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenyltetrahydrofuran-2-carboxamide (Tetrahydrofuranyl fentanyl)[16] |
| 9845 | (1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylcyclopropanecarboxamide (cyclopropyl fentanyl)[19] |
| 7032 | N-(1-amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (MAB-CHMINACA; ADB-CHMINACA)[20] |
| 9840 | N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylpentanamide (valeryl fentanyl)[21] |
| 9823 | N-(4-fluorophenyl)N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)butyramide (para-fluorobutyryl fentanyl)[21] |
| 9837 | N-(4-methoxyphenyl)-N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)butyramide (para-methoxybutyryl fentanyl)[21] |
| 9826 | N-(4-chlorophenyl)-N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)isobutyramide (para-chloroisobutyryl fentanyl)[21] |
| 9827 | N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylisobutyramide (isobutyryl fentanyl)[21] |
| 9847 | N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)-N-phenylcyclopentanecarboxamide (cyclopentyl fentanyl)[21] |
| 9838 | N-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-methoxy-N-(1-phenethylpiperidin-4-yl)acetamide (ocfentanil)[21] |
| 9850 | Fentanyl-related substances, their isomers, esters, ethers, salts and salts of isomers, esters and ethers[22] |
References[edit]
- ^ ab21 CFR1308.11 (CSA Sched I) with changes through 77 FR64032 (Oct 18, 2012). Retrieved September 6, 2013.
- ^21 U.S.C.§ 812(b)(1)United States Code via Cornell University's Legal Information Institute. Retrieved on 2007-10-02.
- ^Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) (22 Jan 2002). 'Title 21 — Food and Drugs Chapter 13 - Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Subchapter I — Control and Enforcement Part D — Offenses and Penalties: Sec. 841. Prohibited Acts A(a)'. Retrieved 23 Oct 2009.
- ^Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (2017). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Placement of Acetyl Fentanyl into Schedule I. Final order'. Federal Register. 82 (108): 26349–51. PMID28591974.
- ^https://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2016-12-14/pdf/2016-29941.pdf
- ^Code of Federal Regulations, 2012-04-01
- ^The first 8 items in the temporary section of the schedule shown on the DEA website are not included here because they are duplicates of entries in the tables above. Presumably, this is because they were made permanent and copied there at some point, but inadvertently not deleted from this temporary listing section.
- ^ abcdDrug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (Feb 10, 2014). 'Schedules of controlled substances: temporary placement of four synthetic cannabinoids into Schedule I. Final order'. Fed. Regist. 79 (27): 7577–7582. PMID24605391.
- ^ abcDrug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (2015). 'Schedules of controlled substances: Temporary placement of three synthetic cannabinoids into schedule I. Final order'. Federal Register. 80 (20): 5042–7. PMID25730924.
- ^ abcDrug Enforcement Administration (2015). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Extension of Temporary Placement of Three Synthetic Phenethylamines in Schedule I. Final order'. Fed. Regist. 80 (219): 70657–9. PMID26567439.
- ^'DEA Schedules Deadly Synthetic Drug U-47700'. November 10, 2016.
- ^Drug Enforcement Administration (2015). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of Acetyl Fentanyl Into Schedule I. Final order'. Fed. Regist. 80 (137): 42381–5. PMID26189217.
- ^Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (2016). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of Furanyl Fentanyl Into Schedule I. Final order'. Fed. Regist. 81 (229): 85873–7. PMID27906535.
- ^ abcdef'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of Six Synthetic Cannabinoids (5F-ADB, 5F-AMB, 5F-APINACA, ADB-FUBINACA, MDMB-CHMICA and MDMB-FUBINACA) Into Schedule I'. Drug Enforcement Administration.
- ^Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (2017). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of Acryl Fentanyl into Schedule I. Temporary scheduling order'. Federal Register. 82 (134): 32453–7. PMID28715161.
- ^ abcDrug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (2017). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of ortho-Fluorofentanyl, Tetrahydrofuranyl Fentanyl, and Methoxyacetyl Fentanyl into Schedule I. Temporary amendment; temporary scheduling order'. Federal Register. 82 (206): 49504–8. PMID29091366.
- ^ abDrug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (2016). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of Butyryl Fentanyl and Beta-Hydroxythiofentanyl into Schedule I. Final order'. Federal Register. 81 (92): 29492–6. PMID27192733.
- ^Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (2017). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of 4-Fluoroisobutyryl Fentanyl into Schedule I. Temporary scheduling order'. Federal Register. 82 (84): 20544–8. PMID28497944.
- ^Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (2018). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of Cyclopropyl Fentanyl in Schedule I. Temporary amendment; temporary scheduling order'. Federal Register. 83 (3): 469–72. PMID29319947.
- ^Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (2018). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Extension of Temporary Placement of MAB–CHMINACA in Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act. Temporary rule; temporary scheduling order; extension'. Federal Register. 83 (20): 4411–2. PMID29461023.
- ^ abcdefgDrug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (2018). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of Seven Fentanyl-Related Substances in Schedule I. Temporary amendment; temporary scheduling order'. Federal Register. 83 (22): 4580–5. PMID29932604.
- ^Drug Enforecement Administration, Department of Justice (2018). 'Schedules of Controlled Substances:Temporary Placement of Fentanyl-Related Substances in Schedule I. Temporary amendment; temporary scheduling order'. Federal Register. 83 (25): 5188–92. PMID29932611.
We often hear that Marijuana is a Schedule 1 drug in the US without stopping to ask what that actually means.
Photo: Dark Web News
Schedule 1 refers to the highest category of illegal or illicit drugs and, for all intents and purposes, are considered to be the most dangerous. The drugs in this category are what are known as 'controlled substances'.
The United States Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) classifies Schedule 1 drugs as having the following characteristics:
Schedule 1 Drugs
The drug or other substance has a high potential for abuse.
The drug or other substance has no currently accepted medical treatment use in the U.S.
There is a lack of accepted safety for use of the drug or substance under medical supervision.
No prescriptions may be written for Schedule I substances, and they are not readily available for clinical use.
Drugs / Substances listed in DEA Schedule 1 include:

- Heroin (diacetylmorphine)
- LSD (Lysergic acid diethylamide)
- Marijuana (cannabis, THC)
- Mescaline (Peyote)
- MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine or “ecstasy”)
- GHB (gamma-hydroxybutyric acid)
- Ecstasy (MDMA or 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine)
- Psilocybin
- Methaqualone (Quaalude)
- Khat (Cathinone)
- Bath Salts (3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone or MDPV)
First of all, I had no idea that people consumed bath salts. I mean, I thought that was something that people sold masquerading as meth. Second, there are a few drugs you might assume to be Schedule 1, like Meth, that are not listed as Schedule 1.
Schedule 2 Drugs
The drug has a high potential for abuse. The drug has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States or a currently accepted medical use with severe restrictions. Abuse of the drug may lead to severe psychological or physical dependence.
Drugs / Substances listed in DEA Schedule 2 include:
- Opium
- Cocaine
- Methamphetamine
- Codeine
- Fentanyl
- Methadone
[There are many more substances on the list but my intention is just to show the most recognizable ones.]
DEA
The DEA has a very difficult time explaining how Marijuana is a Schedule 1 drug; high potential for abuse, no acceptable medical treatment use and is unsafe.
Honestly, how is Fentanyl (50 times more powerful than Heroine) and cause of the current 'heroine crisis' and spiking drug related deaths throughout North America a Schedule 2?
What does more harm? Fentanyl/Heroine Or Marijuana?
Here's a hint, just 3 grains of Fentanyl can be fatal while it's practically impossible to die of a weed overdose.
Fentanyl Makers have made large campaign contributions to prevent recreational marijuana laws from coming into fruition in places like Arizona.
It would seem that the DEA is more concerned with maintaining their own funding, continuing the decades long 'war on drugs' policy failure, incarcerating millions and profiting from asset forfeiture than to confront some of the most basic questions about the US government's own drug policies and incomprehensible drug classifications.